Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Beijing Eagle Sky Pharmatech Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (10) 5979-9429 8875-5821 | |||
 |
sophia_818@126.com contact@eagleskypharmatech.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2009 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Classification | Biochemical >> Inhibitor >> Protein tyrosine kinase |
|---|---|
| Name | L-Glutamyl-L-tryptophan |
| Synonyms | L-alpha-Glutamyl-L-tryptophan; NSC 334073; Oglufanide; Thymogen; Timogen |
| Molecular Structure | 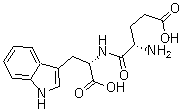 |
| Protein Sequence | EW |
| Molecular Formula | C16H19N3O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 333.34 |
| CAS Registry Number | 38101-59-6 (122933-59-9) |
| SMILES | C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(=CN2)C[C@@H](C(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)N |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 121-122 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 738.9±60.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 400.7±32.9 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.659 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305+P351+P338 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
L‑Glutamyl‑L‑tryptophan is a synthetic dipeptide composed of the amino acids *L‑glutamic acid* and *L‑tryptophan*. It was originally identified as an immunomodulatory factor derived from thymus‑related peptide complexes. The dipeptide has been studied for its role in modulating aspects of immune function in experimental models, particularly in relation to T‑cell responses, neutrophil activity, and natural killer cell‑mediated immune effects. Its structure is simple yet biologically active, placing it among a class of low molecular weight peptides investigated for immune regulation and potential therapeutic effects. The discovery of L‑Glutamyl‑L‑tryptophan traces back to research on thymic extracts, where peptide fractions were isolated from calf thymus tissue. These thymic peptides were found to influence immune cell differentiation and function, and L‑Glutamyl‑L‑tryptophan was identified as one of the key immunomodulatory components within these extracts. Based on this peptide’s activity, a pharmaceutical product known as *Thymogen* was developed, representing a synthesized form of the dipeptide intended to mimic natural thymic peptide activity. The rationale for isolating and synthesizing this dipeptide stemmed from the recognition that shorter peptide fragments could retain biological activity while offering improved stability and reproducibility over complex natural extracts. In early experimental studies, L‑Glutamyl‑L‑tryptophan demonstrated biological activity in animal models. For example, long‑term administration in rodents was shown to influence immune parameters and tumor incidence outcomes. In one study, chronic treatment with the dipeptide in rats was associated with modifications in immune cell activity and a reduced incidence of spontaneous tumors, suggesting that the peptide could modulate processes linked to aging and cancer incidence. These effects were correlated with changes in T‑cell differentiation and chemotactic activities of neutrophils, indicating a broad regulatory influence on innate and adaptive immune pathways. Additional preclinical research examined L‑Glutamyl‑L‑tryptophan’s influence on natural killer (NK) cell‑mediated antitumor activity. In mouse models with genetic alterations affecting immune cell function, the dipeptide’s antitumor effects were dependent on NK cells and related effector mechanisms. This line of investigation suggested that the peptide’s immunomodulatory properties could enhance immune surveillance against tumor formation via specific immune cell subsets. Beyond its effects in oncology‑related models, contemporary research also explored the dipeptide’s potential anti‑inflammatory and tissue‑modulating actions in other biological contexts. In murine models of dermatitis, topical application of L‑Glutamyl‑L‑tryptophan was found to attenuate skin inflammation and modulate cytokine levels, implying immunoregulatory effects beyond classical immune cell activation. These findings point to a complex mechanism of action that may involve modulation of cytokine signaling and immune cell interactions in tissue environments. Mechanistically, the immunomodulatory activity of L‑Glutamyl‑L‑tryptophan is believed to involve enhancement of immune cell recognition and activation pathways, including T‑cell differentiation and neutrophil chemotaxis. Although detailed receptor targets and intracellular signaling pathways remain areas of ongoing study, available evidence indicates that the peptide interacts with immune networks to adjust the balance between immune activation and regulation. Some studies suggest that such small peptides can influence intracellular second messengers, cytokine secretion patterns, and cell surface adhesion molecule expression, contributing to improved immune responsiveness. Historically, the dipeptide and related thymic peptides were investigated extensively in Eastern Europe and Russia as bioregulators of immune dysfunction, with various formulations used in clinical contexts for conditions associated with immune depletion or imbalance. However, the clinical adoption of L‑Glutamyl‑L‑tryptophan‑based products has been regionally variable, and rigorous regulatory evaluation in many jurisdictions remains limited. Research continues to assess both the mechanistic underpinnings and potential translational utility of this and analogous peptides for immune modulation in disease settings. References Anisimov VN, Khavinson VK, Morozov VG (2000) Immunomodulatory synthetic dipeptide L‑Glu‑L‑Trp slows down aging and inhibits spontaneous carcinogenesis in rats. Biogerontology 1(1) 55–59 DOI: 10.1023/A:1010042008969 Morozov VG, Khavinson VK (1997) Natural and synthetic thymic peptides as therapeutics for immune dysfunction. International Journal of Immunopharmacology 19(9–10) 501–505 DOI: 10.1016/S0192-0561(97)00058-1 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for L-Glutamyl-L-tryptophan |