Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Beijing Eagle Sky Pharmatech Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (10) 5979-9429 8875-5821 | |||
 |
sophia_818@126.com contact@eagleskypharmatech.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2009 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Classification | Biochemical >> Peptide |
|---|---|
| Name | Bremelanotide PT 141 |
| Synonyms | N-Acetyl-L-norleucyl-L-alpha-aspartyl-L-histidyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-arginyl-L-tryptophyl-L-lysine (2-7)-lactam |
| Molecular Structure | 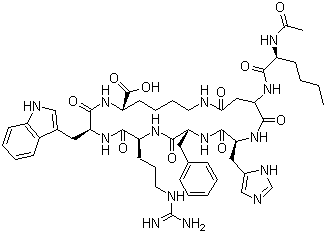 |
| Protein Sequence | XDHFRWK |
| Molecular Formula | C50H68N14O10 |
| Molecular Weight | 1025.16 |
| CAS Registry Number | 189691-06-3 |
| SMILES | CCCC[C@@H](C(=O)N[C@H]1CC(=O)NCCCC[C@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC1=O)CC2=CN=CN2)CC3=CC=CC=C3)CCCN=C(N)N)CC4=CNC5=CC=CC=C54)C(=O)O)NC(=O)C |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Index of refraction | 1.679 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P305+P351+P338 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
Bremelanotide is a **synthetic cyclic heptapeptide** developed as a centrally acting agonist of the melanocortin receptor family. It is structurally derived from analogs of the endogenous neuropeptide hormone α‑melanocyte‑stimulating hormone (α‑MSH) and targets multiple melanocortin receptors, with particular activity at the melanocortin type 4 receptor (MC4R) in the central nervous system. Unlike phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors that primarily act on peripheral vascular pathways, bremelanotide exerts its effects via central neural circuits implicated in sexual desire and motivation. It was approved in 2019 by the United States Food and Drug Administration under the brand name Vyleesi for the treatment of acquired, generalized hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in premenopausal women. The concept behind bremelanotide’s development originated from early research on melanocortinergic peptides and their role in multiple physiological processes, including pigmentation, energy homeostasis, and sexual behavior. Initial work with related compounds such as Melanotan II revealed unexpected effects on sexual arousal pathways, prompting the design of analogs with optimized receptor selectivity and pharmacological profiles tailored for sexual function. Through systematic peptide modification, scientists focused on enhancing central melanocortin receptor agonism while minimizing unwanted melanotropic side effects. This led to the identification of bremelanotide as a promising candidate for addressing sexual desire dysfunction. Bremelanotide is administered by subcutaneous injection, typically at a dose of 1.75 mg delivered at least 45 minutes before anticipated sexual activity. Its mechanism involves activating melanocortin receptors, especially MC4R, in areas of the hypothalamus and limbic system that influence sexual motivation and reward pathways. While the precise cascade of molecular events linking receptor binding to increased sexual desire remains an area of ongoing research, it is believed that bremelanotide modulates central neurotransmitter systems, including dopaminergic signaling, to enhance sexual desire and reduce associated distress. Compared with treatments that rely on daily dosing, bremelanotide’s on‑demand administration provides flexibility aligned with individual needs. Clinical development included multiple randomized, double‑blind, placebo‑controlled phase 3 trials involving premenopausal women diagnosed with HSDD. In these trials, participants exhibited significant improvements in measures of sexual desire and reductions in the distress associated with low desire when treated with bremelanotide compared with placebo over 24 weeks of intermittent dosing. These results supported its regulatory approval and clinical use in carefully selected patient populations. Importantly, the evidence demonstrated that treatment benefits were maintained throughout the study periods, with an acceptable safety profile under supervised conditions. Safety evaluations have identified nausea, flushing, headache, and injection site reactions as the most commonly reported adverse events. Many of these reactions were mild to moderate in intensity and transient. Bremelanotide’s pharmacokinetic profile is characterized by rapid absorption after subcutaneous administration, with peak plasma levels achieved within approximately one hour and a half‑life that supports its on‑demand use. Because bremelanotide can cause transient increases in blood pressure and changes in heart rate, it is contraindicated in individuals with uncontrolled hypertension or known cardiovascular disease, underscoring the importance of careful patient selection and monitoring. Bremelanotide’s approval represents a novel approach to treating sexual desire disorders by targeting central neural pathways rather than peripheral vascular mechanisms. Its development illustrates how insights from basic peptide biology and receptor pharmacology can be translated into clinical therapies addressing unmet medical needs. Ongoing research aims to further clarify its mechanism of action, optimize its use in diverse populations, and explore potential applications beyond the current indication. References New Drug Approved for Treating Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder. Danielle Mayer, Sarah E Lynch (2020) Annals of Pharmacotherapy 54(7) 684–690 DOI: 10.1177/1060028019899152 Bremelanotide for the Treatment of Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder. (2020) Obstetrics & Gynecology 135(3) 555–563 DOI: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003667 Bremelanotide: First Approval. (2019) Drugs 79(17) 1903–1908 DOI: 10.1007/s40265-019-01187-w |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Bremelanotide PT 141 |