Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Zibo Feitian International Trading Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (533) 276-3996 | |||
 |
info@feitianindustry.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2005 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2022 | ||||
| Riverland Trading LLC. | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (336).944-2293 | |||
 |
bens@riverlandtrading.com | |||
| Chemical distributor | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Chiron AS | Norway | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+47 (73) 874-490 | |||
 |
chiron@chiron.no | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| Crescent Chemical Co. Inc. | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 348-0333 | |||
 |
crescent@creschem.com | |||
| Chemical distributor | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Ester >> Octyl ester |
|---|---|
| Name | Dioctyl phthalate |
| Synonyms | Phthalic acid di-n-octyl ester; DOP |
| Molecular Structure | 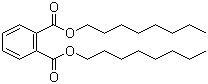 |
| Molecular Formula | C24H38O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 390.56 |
| CAS Registry Number | 117-84-0 |
| EC Number | 204-214-7 |
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCOC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1C(=O)OCCCCCCCC |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 0.98 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | -25 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 416.4±13.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)*, 380 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | 222.3±9.3 ºC (Calc.)*, 103.9 ºC (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.49 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS08 Warning Details
GHS08 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H361 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P203-P280-P318-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 3082 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dioctyl phthalate (DOP), also known as di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, is a synthetic organic compound belonging to the phthalate ester family. Its molecular formula is C24H38O4. Structurally, it is the diester formed from phthalic acid and 2-ethylhexanol, consisting of an aromatic benzene ring bearing two ester-linked branched alkyl chains. Dioctyl phthalate is typically a clear, colorless to pale yellow oily liquid with a faint odor. It is insoluble in water but readily soluble in most organic solvents and compatible with a wide range of polymeric materials. The development of dioctyl phthalate is closely associated with the growth of the plastics industry in the early twentieth century. As poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) emerged as an important synthetic polymer, there was a need for additives that could impart flexibility, softness, and processability to an otherwise rigid material. Phthalate esters were identified as effective plasticizers due to their ability to penetrate polymer chains and reduce intermolecular forces. Dioctyl phthalate became one of the most widely used plasticizers because of its efficiency, low volatility, and favorable compatibility with PVC and related polymers. Industrial production of dioctyl phthalate is achieved by esterification of phthalic anhydride with 2-ethylhexanol. This reaction is typically carried out under acidic catalysis at elevated temperatures, with continuous removal of water to drive the equilibrium toward ester formation. After completion of the reaction, the crude product is purified by neutralization, washing, and vacuum distillation to remove unreacted alcohol, catalyst residues, and low-boiling impurities. The resulting material meets specifications for clarity, viscosity, and purity required for industrial applications. Chemically, dioctyl phthalate functions as a plasticizer by embedding itself between polymer chains, particularly in PVC, increasing chain mobility and reducing the glass transition temperature. The branched alkyl chains contribute to flexibility and durability, while the aromatic phthalate core provides thermal stability. Dioctyl phthalate is relatively stable under normal conditions but can undergo slow hydrolysis under strongly acidic or basic environments, leading to the formation of monoesters and phthalic acid derivatives. In practical applications, dioctyl phthalate has been extensively used as a general-purpose plasticizer for PVC in products such as flexible tubing, cable insulation, flooring, synthetic leather, and coated fabrics. Beyond plastics, it has also been employed as a solvent, hydraulic fluid component, and additive in adhesives, sealants, and inks. Its good electrical insulating properties have supported its use in wire and cable formulations, while its compatibility with rubber and elastomers has made it useful in various molded goods. Physically, dioctyl phthalate exhibits low vapor pressure and good resistance to evaporation, contributing to long-term flexibility in plasticized materials. It remains fluid over a wide temperature range and provides good low-temperature performance to polymers. Storage typically involves keeping the material in tightly sealed containers away from strong oxidizing agents and excessive heat. Standard industrial handling precautions are applied to minimize skin contact and inhalation of aerosols. Over time, increased scientific and regulatory scrutiny has been applied to dioctyl phthalate due to concerns about its environmental persistence and potential health effects. This has led to restrictions or reduced usage in certain consumer applications and encouraged the development of alternative plasticizers. Despite these changes, dioctyl phthalate remains an important historical and industrial chemical that played a central role in the expansion of flexible plastics. Overall, dioctyl phthalate is a benchmark phthalate plasticizer whose discovery and widespread adoption significantly influenced polymer processing and materials engineering. Its effectiveness in imparting flexibility, durability, and workability to plastics established it as a foundational additive in the plastics industry and a reference point for the development of subsequent plasticizer technologies. References 2025. Influence of synergistic plasticization of epoxy 1,6-hexanediol oleate and DOA on the properties of PVC films. Polymer Bulletin. DOI: 10.1007/s00289-025-05787-3 2025. A general strategy for enhancing the migration resistance of plasticizer in poly(vinyl chloride). Journal of Polymer Research. DOI: 10.1007/s10965-025-04323-1 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Dioctyl phthalate |