Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Changzhou Jiuwu Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (519) 8512-1086 +86 13775162768 | |||
 |
info@jiuwuchem.cn | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2009 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2016 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Alcohols, phenols, phenolic compounds and derivatives |
|---|---|
| Name | 3-Amino-6-bromoquinolin-4-ol |
| Molecular Structure | 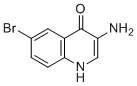 |
| Molecular Formula | C9H7BrN2O |
| Molecular Weight | 239.07 |
| CAS Registry Number | 1153094-27-9 |
| SMILES | C1=CC2=C(C=C1Br)C(=O)C(=CN2)N |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P270-P271-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P312-P330-P362-P403+P233-P501 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
3-Amino-6-bromoquinolin-4-ol is a halogenated quinoline derivative that combines an amino group, a hydroxyl group, and a bromine substituent on a fused heteroaromatic ring system. Compounds of this type belong to the broader family of functionalized quinolinols, which have attracted long-standing interest in medicinal chemistry, dye chemistry, and heterocyclic synthesis. The presence of multiple functional groups on the quinoline scaffold makes this compound a versatile intermediate for further chemical modification and application-driven research. The historical development of 3-amino-6-bromoquinolin-4-ol is closely tied to the exploration of substituted quinolines during the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, when quinoline chemistry emerged as a major field due to its relevance to antimalarial agents, dyes, and metal-chelating compounds. Quinolin-4-ols, in particular, were investigated for their tautomeric behavior and their ability to coordinate metal ions, while amino-substituted quinolines were examined for biological activity. The introduction of halogen atoms such as bromine was later adopted as a strategy to modify electronic properties and reactivity, as well as to enable further cross-coupling reactions. Synthetically, 3-amino-6-bromoquinolin-4-ol is generally obtained through multistep heterocyclic synthesis starting from appropriately substituted aniline or benzene derivatives. Classical approaches involve ring construction via condensation reactions that form the quinoline core, followed by selective functional group transformations. The hydroxyl group at the 4-position is commonly introduced through cyclization routes that favor the quinolin-4-one or quinolin-4-ol framework, while the amino group at the 3-position may arise from nitration followed by reduction or from amination reactions on preformed quinoline intermediates. The bromine substituent is typically introduced by electrophilic bromination at a defined stage of the synthesis or by starting from a brominated precursor to ensure regioselective substitution. The chemical properties of 3-amino-6-bromoquinolin-4-ol are governed by the interplay between its heteroaromatic ring and its substituents. The amino group acts as an electron-donating and hydrogen-bonding functionality, while the hydroxyl group can participate in tautomerism and coordination to metals. The bromine atom contributes to the compound’s lipophilicity and serves as a reactive handle for further derivatization through substitution or coupling reactions. Together, these features make the molecule reactive yet sufficiently stable for isolation and handling under standard laboratory conditions. In terms of applications, 3-amino-6-bromoquinolin-4-ol has primarily been used as an intermediate in organic and medicinal chemistry research. Functionalized quinolinols are frequently explored as precursors to biologically active molecules, including compounds investigated for antimicrobial, antiparasitic, or anticancer properties. While the compound itself may not be widely used as a final pharmaceutical agent, its structural motif is valuable for constructing more complex molecules with tailored biological profiles. The bromine substituent, in particular, enables further elaboration through modern cross-coupling methodologies, allowing researchers to introduce aryl, heteroaryl, or alkyl groups at the 6-position. Beyond medicinal chemistry, derivatives of amino- and hydroxyquinolines have been examined in coordination chemistry and materials science. The ability of the quinolin-4-ol framework to bind metal ions has led to its use in the design of ligands and metal complexes with potential applications in catalysis, sensing, and luminescent materials. In such contexts, 3-amino-6-bromoquinolin-4-ol serves as a useful building block for tuning electronic and steric properties within a ligand system. Overall, 3-amino-6-bromoquinolin-4-ol represents a well-defined example of a multifunctional heterocyclic compound whose importance lies in its role as a synthetic intermediate and research tool. Its development reflects the broader evolution of quinoline chemistry, from early structural studies to modern applications in synthesis and materials-oriented research. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 3-Amino-6-bromoquinolin-4-ol |